 | |
| Type | Set operation |
|---|---|
| Field | Set theory |
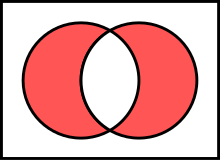
| Statement | The symmetric difference is the set of elements that are in either set, but not in the intersection. |
| Symbolic statement | |
In mathematics, the symmetric difference of two sets, also known as the disjunctive union and set sum, is the set of elements which are in either of the sets, but not in their intersection. For example, the symmetric difference of the sets and is .
The symmetric difference of the sets A and B is commonly denoted by (alternatively, ), , or . It can be viewed as a form of addition modulo 2.
The power set of any set becomes an abelian group under the operation of symmetric difference, with the empty set as the neutral element of the group and every element in this group being its own inverse. The power set of any set becomes a Boolean ring, with symmetric difference as the addition of the ring and intersection as the multiplication of the ring.










