| Synovial joint | |
|---|---|
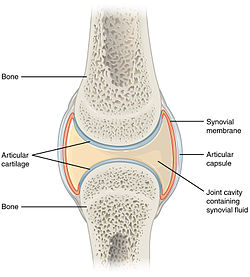 Structure of synovial joint | |
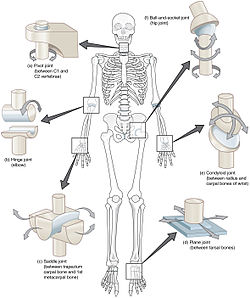 Types of synovial joints.
Clockwise from top-right: ball and socket joint, condyloid joint, plane joint, saddle joint, hinge joint and pivot joint. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | junctura synovialis |
| TA98 | A03.0.00.020 |
| TA2 | 1533 |
| FMA | 7501 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, join bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility.[1] The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid. The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer of fibrous membrane, which keeps the bones together structurally, and an inner layer, the synovial membrane, which seals in the synovial fluid.
They are the most common and most movable type of joint in the body of a mammal. As with most other joints, synovial joints achieve movement at the point of contact of the articulating bones.
- ^ The Musculoskeletal System. In: Dutton M. eds. Dutton's Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, and Intervention, 5e. McGraw-Hill; Accessed January 25, 2021. https://accessphysiotherapy-mhmedical-com.libaccess.lib.mcmaster.ca/content.aspx?bookid=2707§ionid=224662311