| T-tubule | |
|---|---|
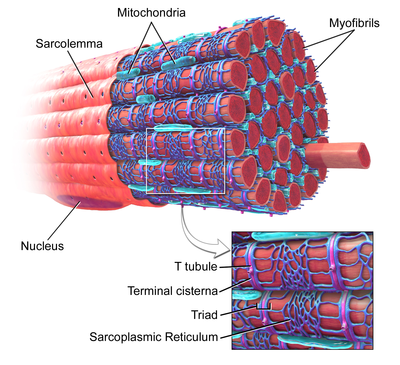 Skeletal muscle fiber, with T-tubule labelled in zoomed in image. | |
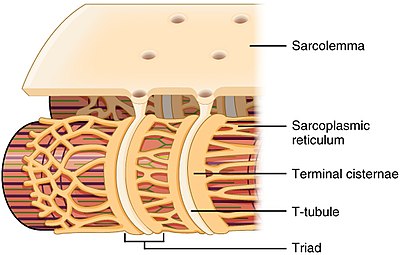 T-tubule structure and relationship to the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Cell membrane of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tubulus transversus |
| TH | H2.00.05.2.01018, H2.00.05.2.02013 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
T-tubules (transverse tubules) are extensions of the cell membrane that penetrate into the center of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. With membranes that contain large concentrations of ion channels, transporters, and pumps, T-tubules permit rapid transmission of the action potential into the cell, and also play an important role in regulating cellular calcium concentration.
Through these mechanisms, T-tubules allow heart muscle cells to contract more forcefully by synchronising calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum throughout the cell.[1] T-tubule structure and function are affected beat-by-beat by cardiomyocyte contraction,[2] as well as by diseases, potentially contributing to heart failure and arrhythmias. Although these structures were first seen in 1897, research into T-tubule biology is ongoing.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Rog-Zielinska EA, et al. (2021). "Beat-by-Beat Cardiomyocyte T-Tubule Deformation Drives Tubular Content Exchange". Circ. Res. 128 (2): 203–215. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317266. PMC 7834912. PMID 33228470.