| TAT-14 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Owners: [1][2]
| |
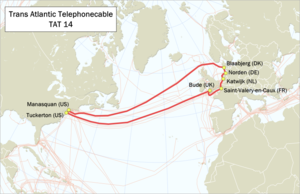
Landing points
| |
| Total length | 15,428 km (9,587 mi) |
| Topology | Self-healing ring |
| Design capacity | 9.38 Tbit/s |
| Currently lit capacity | 3.15 Tbit/s |
| Technology | Fiber optics with EDFA repeaters |
| Date of first use | 21 March 2001 |
| Decommissioning date | 15 December 2020 |
TAT-14 was the 14th consortium transatlantic telecommunications cable system. In operation from 2001 to 2020,[3] it used wavelength division multiplexing. The cable system was built from multiple pairs of fibres—one fibre in each pair was used for data carried in one direction and the other in the opposite direction. Although optical fibre can be used in both directions simultaneously, for reliability it is better not to require splitting equipment at the end of the individual fibre to separate transmit and receive signals—hence a fibre pair is used. TAT-14 used four pairs of fibres—two pairs as active and two as backup. Each fibre in each pair carried 16 wavelengths in one direction, and each wavelength carried up to an STM-256 (38,486,016 kbit/s as payload).[4] The fibres were bundled into submarine cables connecting the United States and the European Union (United Kingdom, France, the Netherlands, Germany, and Denmark) in a ring topology.[5]
By the time this cable went into operation, the expected long boom (term coined by Wired magazine) was already ending in the dot-com death. The overinvestment in transcontinental optical fiber capacity led to a financial crisis in private cable operators like Global Crossing.
In the diplomatic cables leak, it is revealed that the landing point in Katwijk, the Netherlands is included in a US Government list of critical infrastructure susceptible to terrorist attack.[6]
Use of the cable was ceased on December 15, 2020, shortly after the Havfrue cable, whose main trunk also lands at Blaabjerg, was lit in November 2020.[7] In 2021 the permanent dismantling of the system was begun.[8]
- ^ "TAT-14 General Committee". TAT-14 Cable System. Sprint Corporation. Retrieved 18 November 2017.
- ^ "TAT-14". International Network Systems. Retrieved 18 November 2017.
- ^ "Report No. SCL-00267" (PDF). Federal Communications Commission. 2020-04-02. Retrieved December 21, 2020.
the TAT-14 submarine cable will be retired from service on December 15, 2020
- ^ "About the TAT-14 Cable Network". TAT-14. Archived from the original on 2020-08-07. Retrieved 2023-01-14.
- ^ "CABLE LANDING LICENSE". U.S. Federal Communications Commission. 1999-10-01. Retrieved 2013-08-09.
- ^ "VS wijst knelpunten Nederland aan" (in Dutch). RTL Nieuws. 2010-12-06. Archived from the original on 2017-01-01. Retrieved 2013-08-09.
- ^ "Out With the Old Cables, in With the New". 2020-12-21.
- ^ "Upcoming Dismantling of the TAT-14 Submarine Cable System". 2021-05-11.