 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Vyndaqel, Vyndamax, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.246.079 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
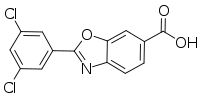
| Formula | C14H7Cl2NO3 |
| Molar mass | 308.11 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Tafamidis, sold under the brand names Vyndaqel and Vyndamax,[5] is a medication used to delay disease progression in adults with certain forms of transthyretin amyloidosis. It can be used to treat both hereditary forms, familial amyloid cardiomyopathy and familial amyloid polyneuropathy, as well as wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis, which formerly was called senile systemic amyloidosis. It works by stabilizing the quaternary structure of the protein transthyretin. In people with transthyretin amyloidosis, transthyretin falls apart and forms clumps called (amyloid) that harm tissues including nerves and the heart.[6][7]
The US Food and Drug Administration considers tafamidis to be a first-in-class medication.[8]
- ^ a b "Vyndamax and Vyndaqel Australian prescription medicine decision summary". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 17 July 2020. Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Vyndaqel". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ "Health product highlights 2021: Annexes of products approved in 2021". Health Canada. 3 August 2022. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
UKlabelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Vyndaqel and Vyndamax labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Vyndaqel EPARwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
FDA PRwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "New Drug Therapy Approvals 2019". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 31 December 2019. Retrieved 15 September 2020.