| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hydroxypropanedioic acid | |
| Other names
tartronic acid,
2-tartronic acid, hydroxymalonic acid, 2-hydroxymalonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.184 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4O5 | |
| Molar mass | 120.06 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.849 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 159 °C (318 °F; 432 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related carboxylic acids
|
Tartaric acid Malic acid Mesoxalic acid Lactic acid 3-Hydroxypropionic acid Malonic acid Propionic acid Oxalic acid |
Related compounds
|
Glyceric acid Glyceraldehyde Tartonaldehyde Glycerol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
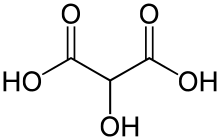
Tartronic acid or 2-hydroxymalonic acid is an organic compound with the structural formula of HOHC(CO2H)2. This dicarboxylic acid is related to malonic acid. It is a white solid. It is produced by oxidation of glycerol:
- HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH + 2 O2 → HO2CCH(OH)CO2H + 2 H2O
Glyceric acid HOCH2CH(OH)CO2H is an intermediate.[1][2]
Its derivative, 2-methyltartronic acid, is isomalic acid.[3]
- ^ Habe, Hiroshi; Fukuoka, Tokuma; Kitamoto, Dai; Sakaki, Keiji (2009). "Biotechnological production of d-glyceric acid and its application". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 84 (3): 445–452. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2124-3. PMID 19621222. S2CID 9144557.
- ^ Yang, Lihua; Li, Xuewen; Chen, Ping; Hou, Zhaoyin (2019). "Selective oxidation of glycerol in a base-free aqueous solution: A short review". Chinese Journal of Catalysis. 40 (7): 1020–1034. doi:10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63301-2. S2CID 196894235.
- ^ Roelofsen, G.; Kanters, J. A.; Kroon, J.; Doesburg, H. M.; Koops, T. (1978). "Order–disorder phenomena in structures of carboxylic acids: The structures of fluoromalonic acid and hydroxymalonic acid at 20 and –150°C". Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry. 34 (8): 2565–2570. Bibcode:1978AcCrB..34.2565R. doi:10.1107/S0567740878008596.
