Chemical element with atomic number 51 (Sb)
Antimony, 51 Sb Pronunciation Appearance silvery lustrous gray
Atomic number (Z ) 51 Group group 15 (pnictogens) Period period 5 Block p-block Electron configuration [Kr ] 4d10 5s2 5p3 Electrons per shell 2, 8, 18, 18, 5 Phase at STP solid Melting point 903.78 K (630.63 °C, 1167.13 °F) Boiling point 1908 K (1635 °C, 2975 °F) Density (at 20° C) 6.694 g/cm3 [ 3] when liquid (at m.p. ) 6.53 g/cm3 Heat of fusion 19.79 kJ/mol Heat of vaporization 193.43 kJ/mol Molar heat capacity 25.23 J/(mol·K) Vapor pressure
P (Pa)
1
10
100
1 k
10 k
100 k
at T (K)
807
876
1011
1219
1491
1858
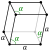
Oxidation states common: −3, +3, +5 ? ? [ 4] ? ? ? Electronegativity Pauling scale: 2.05 Ionization energies 1st: 834 kJ/mol 2nd: 1594.9 kJ/mol 3rd: 2440 kJ/mol (more ) Atomic radius empirical: 140 pm Covalent radius 139±5 pm Van der Waals radius 206 pm Spectral lines of antimonyNatural occurrence primordial Crystal structure rhombohedral (hR2 ) Lattice constants a = 0.45066 nma h = 0.43084 nmc h = 1.12736 nm (at 20 °C)[ 3] Thermal expansion × 10−6 [ a] Thermal conductivity 24.4 W/(m⋅K) Electrical resistivity 417 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) Magnetic ordering diamagnetic [ 5] Molar magnetic susceptibility × 10−6 3 /mol[ 6] Young's modulus 55 GPa Shear modulus 20 GPa Bulk modulus 42 GPa Speed of sound thin rod 3420 m/s (at 20 °C) Mohs hardness 3.0 Brinell hardness 294–384 MPa CAS Number 7440-36-0 Discovery Arabic alchemists (before AD 815) Symbol "Sb": from Latin stibium stibnite '
Category: Antimony references
child table, as reused in {IB-Sb}
^ "Standard Atomic Weights: Antimony" . CIAAW . 1993.^ Prohaska, Thomas; Irrgeher, Johanna; Benefield, Jacqueline; Böhlke, John K.; Chesson, Lesley A.; Coplen, Tyler B.; Ding, Tiping; Dunn, Philip J. H.; Gröning, Manfred; Holden, Norman E.; Meijer, Harro A. J. (2022-05-04). "Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report)" . Pure and Applied Chemistry . doi :10.1515/pac-2019-0603 . ISSN 1365-3075 . ^ a b c Arblaster, John W. (2018). Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of Elements . Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. ISBN 978-1-62708-155-9 ^ Anastas Sidiropoulos (2019). "Studies of N-heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complexes of the Main Group Elements" (PDF) . p. 39. doi :10.4225/03/5B0F4BDF98F60 . S2CID 132399530 . ^ Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). "Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds". CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (PDF) (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5 ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4 ^ a b Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF) . Chinese Physics C . 45 (3): 030001. doi :10.1088/1674-1137/abddae . Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page ).