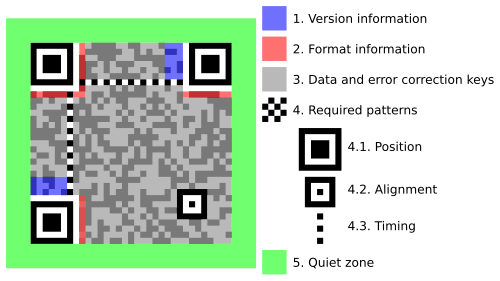
The structure of a quick response (QR) code, a type of matrix barcode that can encode virtually any kind of data. Originally developed for the automotive industry to track vehicles during the manufacturing process, it has since become one of the most popular types of two-dimensional barcodes. The QR code is detected as a 2-dimensional digital image by an image sensor and is then digitally analyzed. The processor locates the three distinctive squares at the corners of the image, and uses a smaller square near the fourth corner to normalize the image for size, orientation, and angle of viewing. The small dots are then converted to binary numbers and validity checked with an error-correcting code.Image: Richard Wheeler