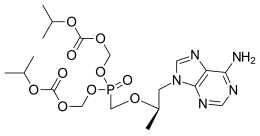
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌtəˈnoʊfəvɪər ˌdɪsəˈprɑːksəl/ |
| Trade names | Viread, others |
| Other names | Bis(POC)PMPA |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a602018 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 25% |
| Metabolism | Ester hydrolysis |
| Metabolites | Tenofovir |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.129.993 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H30N5O10P |
| Molar mass | 519.448 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 9-(2-Phosphonyl-methoxypropyly)adenine (PMPA) |
| MedlinePlus | a602018 |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | < 1% |
| Metabolism | Phosphorylation |
| Metabolites | Tenofovir diphosphate (active metabolite) |
| Elimination half-life | 17 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.129.993 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H14N5O4P |
| Molar mass | 287.216 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Tenofovir disoproxil, sold under the brand name Viread among others, is a medication used to treat chronic hepatitis B and to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS.[4] It is generally recommended for use with other antiretrovirals.[4] It may be used for prevention of HIV/AIDS among those at high risk before exposure, and after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure.[4] It is sold both by itself and together in combinations such as emtricitabine/tenofovir, efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir,[4] and elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir.[5] It does not cure HIV/AIDS or hepatitis B.[4][6] It is available by mouth as a tablet or powder.[4]
Common side effects include nausea, rash, diarrhea, headache, pain, depression, and weakness.[4] Severe side effects include high blood lactate and an enlarged liver.[4] There are no absolute contraindications.[4] It is often recommended during pregnancy and appears to be safe.[4] It is a nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor and works by decreasing the ability of the viruses to replicate.[4]
Tenofovir was patented in 1996 and approved for use in the United States in 2001.[7] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[8] It is available in the United States as a generic medication as of 2017.[9]
- ^ a b "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Prescription medicines: registration of new generic medicines and biosimilar medicines, 2017". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ "Viread EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 5 February 2002. Retrieved 25 May 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 30 November 2016. Retrieved 29 November 2016.
- ^ "Stribild". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 6 February 2022.
- ^ Martin P, Lau DT, Nguyen MH, Janssen HL, Dieterich DT, Peters MG, et al. (November 2015). "A Treatment Algorithm for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: 2015 Update". Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 13 (12): 2071–87.e16. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.007. PMID 26188135.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 505. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "Teva Announces Exclusive Launch of a Generic version of Viread in the United States". www.tevapharm.com. Archived from the original on 6 November 2018. Retrieved 6 November 2018.