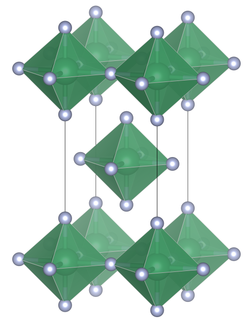
 Unit cell of tin(IV) fluoride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
tin(IV) fluoride
| |
| Other names
stannic fluoride, tin tetrafluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.105 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| SnF4 | |
| Molar mass | 194.704 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | above 700 °C (sublimes) |
| Structure | |
| Tetragonal, tI10 | |
| I4/mmm, No. 139 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Tin(IV) chloride Tin(IV) bromide Tin(IV) iodide |
Other cations
|
Carbon tetrafluoride Silicon tetrafluoride Germanium tetrafluoride Tin tetrafluoride Lead tetrafluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tin(IV) fluoride is a chemical compound of tin and fluorine with the chemical formula SnF4 and is a white solid with a melting point above 700 °C.[1]
SnF4 can be prepared by the reaction of tin metal with fluorine gas:[2]
- Sn + 2F2 → SnF4
However, a passivating metal fluoride layer will be created and the surface will eventually become unreactive. An alternative synthesis is the reaction of SnCl4 with anhydrous hydrogen fluoride:[1]
- SnCl4 + 4HF → SnF4 + 4HCl
With alkali metal fluorides (e.g. KF) hexafluorostannates are produced (e.g.K2SnF6), which contain the octahedral SnF62− anion. SnF4 behaves as a Lewis acid and adducts L2·SnF4 and L·SnF4 have been produced.[2]
- ^ a b Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 381. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
- ^ a b Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E.; Wiberg, N. (2001). Inorganic Chemistry, 1st Edition. Academic Press. p. 908. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.