| Torreya taxifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| A young Torreya taxifolia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Cupressales |
| Family: | Taxaceae |
| Genus: | Torreya |
| Species: | T. taxifolia
|
| Binomial name | |
| Torreya taxifolia | |
| |
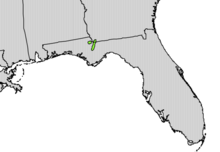
| Native range | |
| Synonyms[3][4][5][6][7] | |
Torreya taxifolia, commonly known as Florida torreya or stinking-cedar, but also sometimes as Florida nutmeg or gopher wood, is an endangered subcanopy tree of the yew family, Taxaceae. It is native to only a small glacial refugium in the southeastern United States, at the state border region of northern Florida and southwestern Georgia.[8]
- ^ Spector, T.; Determann, R.; Gardner, M. (2011). "Torreya taxifolia". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2011: e.T30968A9585489. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2011-2.RLTS.T30968A9585489.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ "Torreya taxifolia. NatureServe Explorer 2.0". explorer.natureserve.org. Retrieved 20 March 2023.
- ^ "Torreya taxifolia Arn". Plants of the World Online. Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 2020. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- ^ Henkel, Johann Baptist [in German]; Hochstetter, Wilhelm Christian [in German] (1865). Synopsis der nadelhölzer, deren charakteristischen merkmale nebst andeutungen über ihre cultur und ausdauer in Deutschlands klima (in German). Vol. 1865. Stuttgart: Verlag der J. G. Cottaschen Buchhandlung. pp. 367, 368. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.15349.
- ^ "Taxus montana". International Plant Names Index. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 2020. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- ^ Nelson, John (under the pseudonym Johannes Senilis) (1866). Pinaceae: being a handbook of the firs and pines. London: Hatchard and co. pp. 167, 168. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.84872.
- ^ Wunderlin, Richard P.; Hansen, Bruce F.; Franck, Alan R.; Essig, F. B. (17 March 2020). "Torreya taxifolia - Species Page". ISB Atlas of Florida Plants. Institute for Systematic Botany, University of South Florida, Tampa. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ "Torreya taxifolia Florida Torreya 5-Year Review: Summary and Evaluation, 2020" (PDF). ecos.fws.gov. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Retrieved 23 June 2022.

