| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
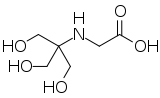
| IUPAC name
N-[1,3-Dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]glycine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
{[1,3-Dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]amino}acetic acid | |
| Other names
Tricine
N-(Tri(hydroxymethyl)methyl)glycine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1937804 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.721 |
| EC Number |
|
| 3688 | |
| MeSH | tricine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H13NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 179.172 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| 89.6 g L−1 (at 20 °C) | |
| UV-vis (λmax) | 260 nm |
| Absorbance | 0.03 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Milacemide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tricine is an organic compound that is used in buffer solutions. The name tricine comes from tris and glycine, from which it was derived.[1] It is a white crystalline powder that is moderately soluble in water. It is a zwitterionic amino acid that has a pKa1 value of 2.3 at 25 °C, while its pKa2 at 20 °C is 8.15. Its useful buffering range of pH is 7.4-8.8. Along with bicine, it is one of Good's buffering agents. Good first prepared tricine to buffer chloroplast reactions.
- ^ Good, N.E., et al., Biochemistry, v. 5, 467 (1966).