| Two-toed sloths[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| Hoffmann's two-toed sloth (C. hoffmanni) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Pilosa |
| Superfamily: | Mylodontoidea |
| Family: | Choloepodidae Gray, 1871[2] |
| Genus: | Choloepus Illiger, 1811[1] |
| Type species | |
| Bradypus didactylus Linnaeus, 1758
| |
| Species | |
| |
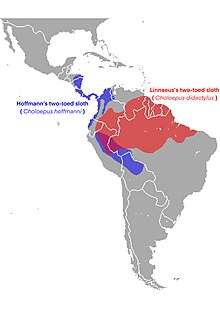
Choloepus is a genus of xenarthran mammals from Central and South America within the monotypic family Choloepodidae, consisting of two-toed sloths,[3] sometimes also called two-fingered sloths.[4] The two species of Choloepus (which means "lame foot"[5]), Linnaeus's two-toed sloth (Choloepus didactylus) and Hoffmann's two-toed sloth (Choloepus hoffmanni), were formerly believed on the basis of morphological studies to be the only surviving members of the sloth family Megalonychidae,[6] but have now been shown by molecular results to be closest to extinct ground sloths of the family Mylodontidae.[4][3]
- ^ a b Gardner, A. L. (2005). "Genus Choloepus". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 101–102. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Anderson, S. (1997). "Mammals of Bolivia, Taxonomy and Distribution". Bulletin of the AMNH (231): 168.
- ^ a b Presslee, S.; Slater, G. J.; Pujos, F.; Forasiepi, A. M.; Fischer, R.; Molloy, K.; et al. (2019). "Palaeoproteomics resolves sloth relationships" (PDF). Nature Ecology & Evolution. 3 (7): 1121–1130. Bibcode:2019NatEE...3.1121P. doi:10.1038/s41559-019-0909-z. PMID 31171860. S2CID 174813630. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 September 2020. Retrieved 18 September 2020.
- ^ a b Delsuc, F.; Kuch, M.; Gibb, G. C.; Karpinski, E.; Hackenberger, D.; Szpak, P.; Martínez, J. G.; Mead, J. I.; McDonald, H. G.; MacPhee, R.D.E.; Billet, G.; Hautier, L.; Poinar, H. N. (2019). "Ancient Mitogenomes Reveal the Evolutionary History and Biogeography of Sloths". Current Biology. 29 (12): 2031–2042.e6. Bibcode:2019CBio...29E2031D. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2019.05.043. hdl:11336/136908. PMID 31178321.
- ^ "Sloth-World.org". Archived from the original on 2 February 2009.
- ^ Myers, Phil (2001). "Family Megalonychidae: two-toed sloths". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on 11 March 2017. Retrieved 11 March 2017.