| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Uranium(VI) chloride
| |
| Other names
Uranium hexachloride
Peruranic chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
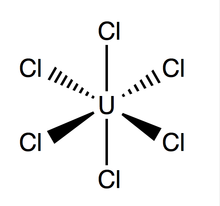
| UCl6 | |
| Molar mass | 450.745 g/mol |
| Appearance | dark green crystalline solid |
| Density | 3.6 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 177 °C (351 °F; 450 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Uranium hexafluoride |
Other cations
|
Tungsten hexachloride |
Related uranium chlorides
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Uranium hexachloride (UCl6) is an inorganic chemical compound of uranium in the +6 oxidation state.[1][2] UCl6 is a metal halide composed of uranium and chlorine. It is a multi-luminescent dark green crystalline solid with a vapor pressure between 1-3 mmHg at 373.15 K.[3] UCl6 is stable in a vacuum, dry air, nitrogen and helium at room temperature. It is soluble in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Compared to the other uranium halides, little is known about UCl6.
- ^ Zachariasen, W. H. (1948). "Crystal chemical studies of the 5f-series of elements. V. The crystal structure of uranium hexachloride". Acta Crystallographica. 1 (6): 285–287. Bibcode:1948AcCry...1..285Z. doi:10.1107/S0365110X48000788.
- ^ Taylor, J. C.; Wilson, P. W. (1974). "Neutron and X-ray powder diffraction studies of the structure of uranium hexachloride". Acta Crystallographica Section B. 30 (6): 1481. Bibcode:1974AcCrB..30.1481T. doi:10.1107/S0567740874005115.
- ^ Van Dyke, R. E.; Evers, E. C. (1955). "Preparation of Uranium Hexachloride". Google Patents: 2.