| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bis(η8-cyclooctatetraenyl)uranium(IV)
| |||
| Other names
Uranium cyclooctatetraenide
U(COT)2 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C16H16U | |||
| Molar mass | 446.33 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | green crystals[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
pyrophoric, radioactive, and toxic | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
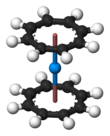
Uranocene, U(C8H8)2, is an organouranium compound composed of a uranium atom sandwiched between two cyclooctatetraenide rings. It was one of the first organoactinide compounds to be synthesized. It is a green air-sensitive solid that dissolves in organic solvents. Uranocene, a member of the "actinocenes," a group of metallocenes incorporating elements from the actinide series. It is the most studied bis[8]annulene-metal system, although it has no known practical applications.[2]
- ^ Streitwieser, A.; Mueller-Westerhoff, U. (1968). "Bis(cyclooctatetraenyl)uranium (uranocene). A new class of sandwich complexes that utilize atomic f orbitals". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 90 (26): 7364. doi:10.1021/ja01028a044.
- ^ Seyferth, D. (2004). "Uranocene. The First Member of a New Class of Organometallic Derivatives of the f Elements". Organometallics. 23 (15): 3562–3583. doi:10.1021/om0400705.