| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
phosphoric acid;urea
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.149 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH7N2O5P | |
| Molar mass | 158.050 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
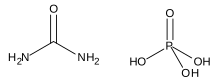
Urea phosphate is a 1:1 combination of urea and phosphoric acid that is used as a fertilizer. It has an NPK formula of 17-44-0,[1] and is soluble in water, producing a strongly acidic solution.
Urea phosphate is available in fertilizer vendor bags that carry a UP signet on the packaging. It is sometimes added to blends which contain calcium nitrate, magnesium nitrate and potassium nitrate to produce water-soluble formulas such as 15-5-15 and 13-2-20. The acidity of urea phosphate allows Ca, Mg and P to co-exist in solution. Under less acidic conditions, there would be precipitation of Ca–Mg phosphates. Urea phosphate is often used in drip irrigation to clean pipe systems.[2][3]
The phosphoric acid and urea molecules in the urea phosphate crystal structure form a complex hydrogen-bonding network,[4] with the hydrogen atoms bonding more strongly to urea molecules.[5] It freely dissociates when dissolved in water.
Urea phosphate is produced as a non-ionic adduct of urea and phosphoric acid,[6] with the typical 17-44-0 grade of fertilizer produced using wet process phosphoric acid at concentrations that vary from 54%[1] to 90%:[7]
H3PO4(aq) + (NH2)2CO(s) → (NH2)2CO · H3PO4(s)
- ^ a b Stinson, John M. (1977). Purified Liquid Fertilizers from Wet-process Acid Via Solid Urea Phosphate. National Fertilizer Development Center, Tennessee Valley Authority. p. 3.
- ^ Ramachandrula, Venkata Ramamohan; Kasa, Ramamohan Reddy (2022-10-01). "Prevention and treatment of drip emitter clogging: a review of various innovative methods". Water Practice and Technology. 17 (10): 2059–2070. doi:10.2166/wpt.2022.115. ISSN 1751-231X.
- ^ Stroehlein, J. L.; Rubeiz, I. G.; Oebker, N. F. (April 1986). "Urea Phosphate Applied by Subsurface Drip Irrigation Increases Availability of Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus". Vegetable Report. hdl:10150/214135.
- ^ Sundera-Rao, R. V. G.; Turley, J. W.; Pepinsky, R. (1957). "The crystal structure of urea phosphate". Acta Crystallogr. 10 (6): 435–436. Bibcode:1957AcCry..10..435S. doi:10.1107/S0365110X57001425.
- ^ Rodrigues, Bernardo Lages; Tellgren, Roland; Fernandes, Nelson G. (2001-06-01). "Experimental electron density of urea–phosphoric acid (1/1) at 100 K". Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Science. 57 (3): 353–358. doi:10.1107/S0108768101004359. ISSN 0108-7681.
- ^ Lagier, Claudia M.; Zuriaga, Mariano; Monti, Gustavo; Olivieri, Alejandro C. (September 1996). "Urea-phosphoric acid complex studied by variable temperature 31P NMR spectroscopy and semiempirical calculations". Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids. 57 (9): 1183–1190. Bibcode:1996JPCS...57.1183L. doi:10.1016/0022-3697(95)00294-4.
- ^ Jančaitienė, Kristina; Medekšaitė, Agnė; Šlinkšienė, Rasa (2023-11-14). "Influence of the Process Parameters on the Synthesis of Urea Phosphate and the Properties of the Obtained Product". Crystals. 13 (11): 1584. doi:10.3390/cryst13111584. ISSN 2073-4352.