This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (August 2012) |
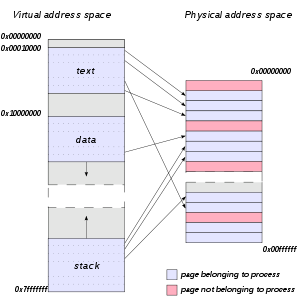
In computing, a virtual address space (VAS) or address space is the set of ranges of virtual addresses that an operating system makes available to a process.[1] The range of virtual addresses usually starts at a low address and can extend to the highest address allowed by the computer's instruction set architecture and supported by the operating system's pointer size implementation, which can be 4 bytes for 32-bit or 8 bytes for 64-bit OS versions. This provides several benefits, one of which is security through process isolation assuming each process is given a separate address space.
- ^ "What is an address space?". IBM. Retrieved May 5, 2024.