This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. (December 2019) |
| volt-ampere | |
|---|---|
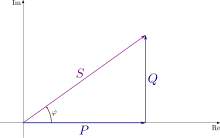 Apparent power () is the magnitude of the vector sum of real power vector () and reactive power vector (); is the phase shift between voltage and current. | |
| General information | |
| Unit system | SI units |
| Unit of | Apparent power |
| Symbol | V⋅A |
| Conversions | |
| 1 V⋅A in ... | ... is equal to ... |
| SI base units | 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3 |
The volt-ampere (SI symbol: VA,[1] sometimes V⋅A or V A) is the unit of measurement for apparent power in an electrical circuit. It is the product of the root mean square voltage (in volts) and the root mean square current (in amperes).[2] Volt-amperes are usually used for analyzing alternating current (AC) circuits. In direct current (DC) circuits, this product is equal to the real power, measured in watts.[3] The volt-ampere is dimensionally equivalent to the watt: in SI units, 1 V⋅A = 1 W. VA rating is most used for generators and transformers, and other power handling equipment, where loads may be reactive (inductive or capacitive).
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
dirwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Ciletti, M. D., Irwin, J. D., Kraus, A. D., Balabanian, N., Bickard, T. A., and Chan, S. P. (1993). Linear circuit analysis. In Electrical Engineering Handbook, edited by R. C. Dorf. Boca Raton: CRC Press. (pp.82–87)
- ^ IEEE 100 : the authoritative dictionary of IEEE standards terms.-7th ed. ISBN 0-7381-2601-2, page 14



