This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
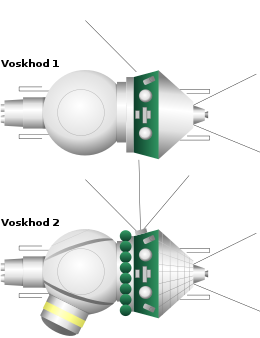 Voskhod 1 and 2 spacecraft | |
| Manufacturer | OKB-1 |
|---|---|
| Designer | Sergei Korolev |
| Country of origin | Soviet Union |
| Operator | OKB-1 (Now RKK Energia) |
| Applications | Human spaceflight |
| Specifications | |
| Spacecraft type | Crewed |
| Launch mass | 5686kg |
| Crew capacity | 3 and 2 |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 5 m |
| Production | |
| Status | Retired |
| Built | 5+ |
| Launched | 5 |
| Retired | 5 |
| Maiden launch | 6 October 1964 |
| Last launch | 18 March 1965 |
| Related spacecraft | |
| Derived from | Vostok |
| Derivatives | Bion |
The Voskhod (Russian: Восход, "Sunrise") was a spacecraft built by the Soviet Union's space program for human spaceflight as part of the Voskhod programme. It was a development of and a follow-on to the Vostok spacecraft. Voskhod 1 was used for a three-man flight whereas Voskhod 2 had a crew of two. They consisted of a spherical descent module (diameter 2.3 metres (7.5 ft)), which housed the cosmonauts, and instruments, and a conical equipment module (mass 2.27 tonnes or 5,000 pounds, 2.25 m (7.4 ft) long, 2.43 m (8.0 ft) wide), which contained propellant and the engine system. Voskhod was superseded by the Soyuz spacecraft in 1967.