This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2019) |
| Weissella | |
|---|---|
| |
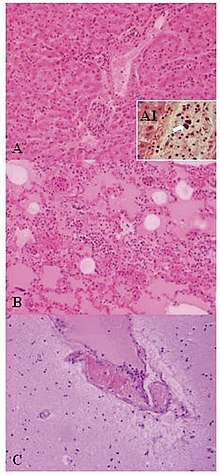
| Lesions of Weissella confusa in the mona monkey (hematoxylin and eosin stain): A) liver: portal triads with neutrophilic infiltration (x10); A1, presence of bacterial emboli inside the vein (arrow) (x40). B) acute pneumonia: edema, congestion, and leukocyte cells exudation in the pulmonary alveoli (x10). C) encephalitis: congestion and marginalized neutrophils in nervous vessels (x10) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Weissella Collins et al. 1994[2]
|
| Type species | |
| Weissella viridescens (Niven and Evans 1957) Collins et al. 1994[2]
| |
Weissella[3] is a genus of gram-positive bacteria placed within the family Lactobacillaceae, formerly considered species of the Leuconostoc paramesenteroides group.[2] The morphology of Weissella species varies from spherical or lenticular cells to irregular rods.[citation needed] Several strains of Weissella cibaria and Weissella confusa have shown probiotic potential.[4] In particular, the cell-free culture supernatant of Weissella confusa shows a number of beneficial characteristics, such as antibacterial potential and anti-inflammatory efficiency.[5] However, several strains of W. confusa are opportunistic bacteria. A number of studies have been done on the safety of the bacterial species, indicating their probiotic potential.[6][7] The Senate Commission on Food Safety has validated the use of W. confusa in food.[8]
- ^ Zheng J, Wittouck S, Salvetti E, Franz CMAP, Harris HMB, Mattarelli P, O'Toole PW, Pot B, Vandamme P, Walter J, Watanabe K, Wuyts S, Felis GE, Gänzle MG, Lebeer S. (2020). "A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae". Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 70 (4): 2782–2858. doi:10.1099/ijsem.0.004107. hdl:10067/1738330151162165141. PMID 32293557.
- ^ a b c Collins, M.D.; Samelis, J.; Metaxopoulos, J.; Wallbanks, S. (1993). "Taxonomic studies on some leuconostoc-like organisms from fermented sausages: Description of a new genus Weissella for the Leuconostoc paramesenteroides group of species". Journal of Applied Microbiology. 75 (6): 595–603. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.1993.tb01600.x. ISSN 1364-5072. PMID 8294308.
- ^ Björkroth, Johanna; Holzapfel, Wilhelm (2006). "Genera Leuconostoc, Oenococcus and Weissella". The Prokaryotes. pp. 267–319. doi:10.1007/0-387-30744-3_9. ISBN 978-0-387-25494-4.
- ^ Lee, Kang Wook; Park, Ji Yeong; Jeong, Hee Rok; Heo, Ho Jin; Han, Nam Soo; Kim, Jeong Hwan (2012). "Probiotic properties of Weissella strains isolated from human faeces". Anaerobe. 18 (1): 96–102. doi:10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.12.015. PMID 22200451. S2CID 30531783.
- ^ Dey, Debasish Kumar; Khan, Imran; Kang, Sun Chul (2019). "Anti-bacterial susceptibility profiling of Weissella confusa DD_A7 against the multidrug-resistant ESBL-positive E. coli". Microbial Pathogenesis. 128: 119–130. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2018.12.048. PMID 30597254. S2CID 58591071.
- ^ Panthee, S; Paudel, A; Blom, J; Hamamoto, H; Sekimizu, K (2019). "Complete genome sequence of Weissella hellenica 0916-4-2 and its comparative genomic analysis". Frontiers in Microbiology. 10: 1619. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2019.01619. PMC 6667553. PMID 31396169.
- ^ Dey, Debasish Kumar; Koo, Bon Gyo; Sharma, Chanchal; Kang, Sun Chul (2019). "Characterization of Weissella confusa DD_A7 isolated from kimchi". LWT. 111: 663–672. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2019.05.089. S2CID 182815194.
- ^ Vogel, R. F.; Hammes, W. P.; Habermeyer, M.; Engel, K. H.; Knorr, D.; Eisenbrand, G.; Senate Commission on Food Safety (SKLM) of the German Research Foundation (2011). "Microbial food cultures--opinion of the Senate Commission on Food Safety (SKLM) of the German Research Foundation (DFG)". Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. 55 (4): 654–62. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201100010. PMID 21351251.