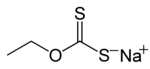


A xanthate is a salt or ester of a xanthic acid. The formula of the salt of xanthic acid is [R−O−CS2]−M+ (where R is organyl group and M is usually Na or K).[1] Xanthate also refers to the anion [R−O−CS2]−. The formula of a xanthic acid is R−O−C(=S)−S−H, such as ethyl xanthic acid, while the formula of an ester of a xanthic acid is R−O−C(=S)−S−R', where R and R' are organyl groups. The salts of xanthates are also called O-organyl dithioates. The esters of xanthic acid are also called O,S-diorganyl esters of dithiocarbonic acid. The name xanthate is derived from Ancient Greek ξανθός (xanthos) meaning 'yellowish' or 'golden', and indeed most xanthate salts are yellow. They were discovered and named in 1823 by Danish chemist William Christopher Zeise. These organosulfur compounds are important in two areas: the production of cellophane and related polymers from cellulose and (in mining) for extraction of certain sulphide bearing ores.[2] They are also versatile intermediates in organic synthesis.
- ^ IUPAC does not recommend the use of the term xanthate, although it is in current use in the scientific literature: IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Xanthate". doi:10.1351/goldbook.X06696
- ^ Roy, Kathrin-Maria. "Xanthates". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a28_423. ISBN 978-3527306732.