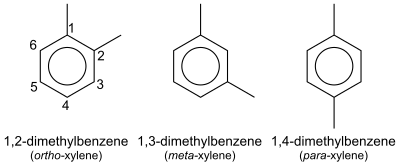
In organic chemistry, xylene or xylol (from Greek ξύλον (xylon) 'wood';[1][2] IUPAC name: dimethylbenzene) are any of three organic compounds with the formula (CH3)2C6H4. They are derived from the substitution of two hydrogen atoms with methyl groups in a benzene ring; which hydrogens are substituted determines which of three structural isomers results. It is a colorless, flammable, slightly greasy liquid of great industrial value.[3]
The mixture is referred to as both xylene and, more precisely, xylenes. Mixed xylenes refers to a mixture of the xylenes plus ethylbenzene. The four compounds have identical molecular formulas C8H10. Typically the four compounds are produced together by various catalytic reforming and pyrolysis methods.[4]
- ^ ξύλον. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project.
- ^ Harper, Douglas. "xylene". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ullmannwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cannella, William J. (2000). "Xylenes and Ethylbenzene". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.2425120503011414.a01. ISBN 0471238961.