 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Reclast, Zometa, others[1] |
| Other names | zoledronate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a605023 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| Drug class | Bisphosphonate[3] |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 22% |
| Metabolism | Nil |
| Elimination half-life | 146 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (partial) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
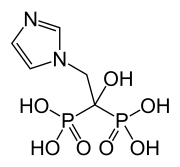
| Formula | C5H10N2O7P2 |
| Molar mass | 272.090 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Zoledronic acid, also known as zoledronate and sold under the brand name Zometa among others,[7] by Novartis among others, is a medication used to treat a number of bone diseases.[3] These include osteoporosis, high blood calcium due to cancer, bone breakdown due to cancer, Paget's disease of bone[3] and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). It is given by injection into a vein.[3]
Common side effects include fever, joint pain, high blood pressure, diarrhea, and feeling tired.[3] Serious side effects may include kidney problems, low blood calcium, and osteonecrosis of the jaw.[3] Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby.[3] It is in the bisphosphonate family of medications.[3] It works by blocking the activity of osteoclast cells and thus decreases the breakdown of bone.[3]
Zoledronic acid was patented in 1986 and approved for medical use in the United States in 2001.[3][8] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[9]
- ^ "International trade names for zoledronic acid". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- ^ "Zoledronic acid Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 1 June 2020. Archived from the original on 16 November 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Zoledronic Acid". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 15 December 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- ^ "Reclast- zoledronic acid injection, solution". DailyMed. 7 July 2022. Retrieved 10 August 2024.
- ^ "Zometa EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 20 March 2001. Archived from the original on 7 June 2023. Retrieved 5 July 2024. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ "Aclasta EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 15 April 2005. Retrieved 10 August 2024. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ "Novartis's Reclast Receives FDA Approval for Women With Postmenopausal Osteoporosis". FierceBiotech (Press release). 20 August 2007. Archived from the original on 28 March 2018. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 524. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 14 January 2023. Retrieved 2 June 2020.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.