 | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Siding Spring Srvy. |
| Discovery site | Siding Spring Obs. |
| Discovery date | 1 April 2005 |
| Designations | |
| (308242) 2005 GO21 | |
| Aten · NEO · PHA[2] | |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 3385 days (9.27 yr) |
| Aphelion | 1.0093 AU (150.99 Gm) |
| Perihelion | 0.49720 AU (74.380 Gm) |
| 0.75324 AU (112.683 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.33992 |
| 0.65 yr (238.8 d) | |
| 19.462° | |
| 1.5077°/day | |
| Inclination | 24.926° |
| 272.70° | |
| 156.62° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0452219 AU (6.76510 Gm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| ~1.6 km[3] | |
| 11.00 h[2][3] | |
| 16.5[2] | |
(308242) 2005 GO21 is a large Aten near-Earth asteroid and potentially hazardous object.[2] It has a well determined orbit with an observation arc of 7 years and an uncertainty parameter of 0.[2] It was discovered on 1 April 2005 by the Siding Spring Survey at an apparent magnitude of 18.1 using the 0.5-metre (20 in) Uppsala Southern Schmidt Telescope.[1]
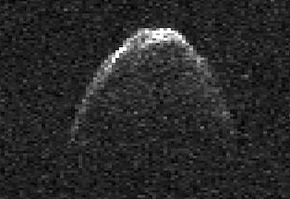
Based on an absolute magnitude of 16.4,[2] the asteroid has an estimated diameter of 1.6 km (within a factor of two).[3] (308242) 2005 GO21 is the largest potentially hazardous asteroid (PHA) discovered in 2005.[4] On 21 June 2012 it passed Earth at a distance of 0.043963 AU (6,576,800 km; 4,086,600 mi).[5] The 2012 passage was studied with radar using Goldstone and Arecibo.[3]
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
MPEC2005-G31was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g Cite error: The named reference
jpldatawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
Goldstonewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
jpl-searchwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
jpl-closewas invoked but never defined (see the help page).