| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
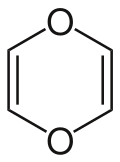
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4-Dioxine[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,4-Dioxacyclohexa-2,5-diene | |||
| Other names
1,4-Dioxin
Dioxin p-Dioxin 1,4-Dioxa[6]annulene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 84.07 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Boiling point | 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
highly flammable | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
1,2-dioxin, dibenzodioxin | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
1,4-Dioxin (also referred as dioxin or p-dioxin) is a heterocyclic, organic, non-aromatic[2] compound with the chemical formula C4H4O2. There is an isomeric form of 1,4-dioxin, 1,2-dioxin (or o-dioxin). 1,2-Dioxin is very unstable due to its peroxide-like characteristics.
The term "dioxin" is most commonly used for a family of derivatives of dioxin, known as polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs).
- ^ "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 147. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Science of Synthesis: Houben-Weyl Methods of Molecular Transformations Vol. 16: Six-Membered Hetarenes with Two Identical Heteroatoms