| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
401 members of the Electoral College 201 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 77.5%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
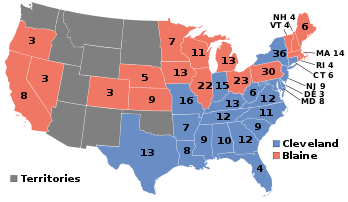 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes those won by Cleveland/Hendricks, red denotes states won by Blaine/Logan. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1884 United States presidential election was the 25th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 4, 1884. In the election, Governor Grover Cleveland of New York narrowly defeated Republican James G. Blaine of Maine. It was set apart by mudslinging and personal allegations that eclipsed substantive issues, such as civil administration change. Cleveland was the first Democrat elected president of the United States since James Buchanan in 1856, the first to hold office since Andrew Johnson left the White House in 1869, and the last to hold office until Woodrow Wilson, who began his first term in 1913. For this reason, 1884 is a significant election in U.S. political history, marking an interruption in the era when Republicans largely controlled the presidency between Reconstruction and the Great Depression.
Cleveland won the presidential nomination on the second ballot of the 1884 Democratic National Convention. President Chester A. Arthur had acceded to the presidency in 1881 following the assassination of James A. Garfield, but he was unsuccessful in his bid for nomination to a full term. Blaine, who had served as Secretary of State under President Garfield, defeated Arthur and other candidates on the fourth ballot of the 1884 Republican National Convention. A group of reformist Republicans known as "Mugwumps" abandoned Blaine's candidacy, viewing him as corrupt. The campaign was marred by exceptional political acrimony and personal invective. Blaine's reputation for public corruption and his inadvertent last minute alienation of Catholic voters proved decisive, as well as general voter burnout after a generation of Republican rule.
In the election, Cleveland won 48.8% of the nationwide popular vote and 219 electoral votes, carrying the Solid South and several key swing states. Blaine won 48.3% of the popular vote and 182 electoral votes. Cleveland won his home state by just 1,149 votes. Two third-party candidates, John St. John of the Prohibition Party and Benjamin Butler of the Greenback Party and the Anti-Monopoly Party, each won less than 2% of the popular vote. Blaine was the last former secretary of state to be nominated by a major political party until the nomination of Hillary Clinton in 2016, while Cleveland, who would be elected to another non-consecutive term in 1892, became the only Democratic president between the end of the Civil War and the election of Woodrow Wilson in 1912, a span of almost 50 years. Blaine, similarly, also became the only Republican nominee in the 56-year period between 1860 and 1916 never to win a presidential election, and just one of three nominees from that party never to win the presidency in the 80 year span between 1856 and 1936. This election is the only time that both vice presidential candidates would die before the next election.
- ^ "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections". The American Presidency Project. UC Santa Barbara.

