| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 58.8% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
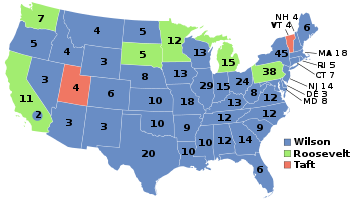 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Wilson/Marshall, light green denotes those won by Roosevelt/Johnson, red denotes those won by Taft/Butler. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1912 United States presidential election was the 32nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 5, 1912. Democratic governor Woodrow Wilson of New Jersey unseated incumbent Republican president William Howard Taft while defeating former president Theodore Roosevelt (who ran under the banner of the new Progressive/"Bull Moose" Party) and Socialist Party nominee Eugene V. Debs.[1]
Roosevelt served as president from 1901 to 1909 as a Republican, and Taft succeeded him with his support. Taft's conservatism angered Roosevelt, so he challenged Taft for the party nomination at the 1912 Republican National Convention. When Taft and his conservative allies narrowly prevailed, Roosevelt rallied his progressive supporters and launched a third-party bid. At the Democratic Convention, Wilson won the presidential nomination on the 46th ballot, defeating Speaker of the House Champ Clark and several other candidates with the support of William Jennings Bryan and other progressive Democrats. The Socialist Party renominated its perennial standard-bearer, Eugene V. Debs.
The general election was bitterly contested by Wilson, Roosevelt, Taft and Debs. Roosevelt's "New Nationalism" platform called for social insurance programs, reduction to an eight-hour workday, and robust federal regulation of the economy. Wilson's "New Freedom" platform called for tariff reduction, banking reform, and new antitrust regulation. Incumbent Taft conducted a subdued campaign based on his platform of "progressive conservatism". Debs, who was attempting to gain widespread support for his socialist policies, claimed that Wilson, Roosevelt and Taft were all financed by different factions within the capitalist trusts, and that Roosevelt in particular was a demagogue using socialistic language in order to divert socialist policies up safe channels for the capitalist establishment.
The Republican split enabled Wilson to win 40 states and a landslide victory in the electoral college with just 41.8% of the popular vote, the lowest vote share for a victorious presidential candidate since 1860. Wilson was the first Democrat to win a presidential election since 1892 as well as the first presidential candidate to receive over 400 electoral votes in a presidential election. Roosevelt finished second with 88 electoral votes and 27% of the popular vote. Taft carried 23% of the national vote and won two states, Vermont and Utah. Debs, the fourth-place finisher, won no electoral votes but received 6% of the popular vote, which remains the highest percentage of the vote ever won by a socialist candidate in the history of US presidential elections. This is the most recent presidential election, and the first since 1876, in which the Democratic ticket has consisted of sitting governors.
- ^ Morris, Edmund. Colonel Roosevelt. New York: Random House Trade Paperbacks. pp. 215, 646.



