| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 86.21% (first round) 83.45% (second round) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
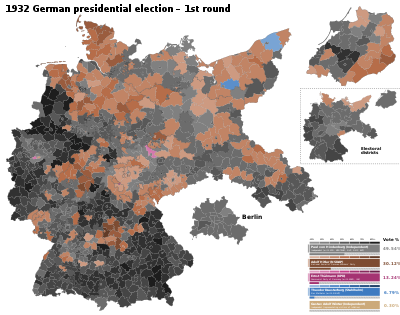
Presidential elections were held in Germany on 13 March 1932, with a runoff on 10 April.[1] Independent incumbent Paul von Hindenburg won a second seven-year term against Adolf Hitler of the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Communist Party (KPD) leader Ernst Thälmann also ran and received more than ten percent of the vote in the runoff. Theodor Duesterberg, the deputy leader of the World War I veterans' organization Der Stahlhelm, ran in the first round but dropped out of the runoff. This was the second and final direct election to the office of President of the Reich (Reichspräsident), Germany's head of state under the Weimar Republic.
Under the Weimar Republic, which had arisen from Germany's defeat in World War I, the presidency was a powerful office. Although the Weimar Constitution had provided for a semi-presidential republic, structural weaknesses and political polarization had resulted in a paralyzed Reichstag. Combined with the Great Depression, this resulted in a government that had governed exclusively via presidential decrees since March 1930, giving the President much power. Hindenburg had been elected to the office in 1925 with the support of a coalition of several parties on the right who hoped that he would overturn the Weimar Republic, which was never particularly popular.
The Nazi Party had risen very rapidly, from being a fringe group for much of the 1920s to becoming the second-largest party in the Reichstag in 1930. Led by Hitler, who exercised sole control over its policy and direction, its ideology combined extreme hostility towards the Weimar Republic with fervent antisemitism, anti-communism and German nationalism. The threat of Hitler caused many on the left to support Hindenburg; at the same time, Hindenburg's failure to overturn the Weimar Republic had disappointed many of those on the right who had supported him in 1925. The combined effect of these two influences resulted in a drastic change of Hindenburg's voter base between the two elections. In 1925 he had been elected as the right-wing candidate, while in 1932 much of his support came from the centre and left. Some on the left were still lukewarm towards Hindenburg; the Communists exploited this by running Thälmann and promoting him as "the only left candidate". Hindenburg failed to receive the requisite majority of votes in the first round, but was able to win reelection in the runoff.
Hindenburg's reelection failed to prevent the NSDAP from assuming power. Two successive federal elections later that year left it as the largest party in the Reichstag, and anti-republic parties in general holding the majority of seats. Under this political climate, Hindenburg appointed Hitler as Chancellor of Germany in January 1933. Upon Hindenburg's death in 1934 Hitler de facto assumed the presidency, which he combined with the chancellorship to become the Führer und Reichskanzler. Therefore, the 1932 election was the last presidential election in Germany until 1949 (by which point the country was divided into West Germany and East Germany). It remains, until today, the last direct election of the German President. All presidential elections after World War II have been indirect. Hindenburg remained the only independent politician elected president of Germany until the election of Joachim Gauck nearly 80 years later.
- ^ Nohlen & Stöver, p. 762