| 1p36 deletion syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Monosomy 1p36 |
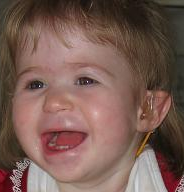 | |
| A toddler showing facial symptoms of the syndrome. | |
| Differential diagnosis | Rett syndrome, Angelman syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome |
| Frequency | 1 in 5,000 to 1 in 10,000 |
1p36 deletion syndrome is a congenital genetic disorder characterized by moderate to severe intellectual disability, delayed growth, hypotonia, seizures, limited speech ability, malformations, hearing and vision impairment, and distinct facial features. The symptoms may vary, depending on the exact location of the chromosomal deletion.[1]
The condition is caused by a genetic deletion (loss of a segment of DNA) on the outermost band on the short arm (p) of chromosome 1. It is one of the most common deletion syndromes. The syndrome is thought to affect one in every 5,000 to 10,000 births.[2]
- ^ "Chromosome 1, 1p36 deletion syndrome". WrongDiagnosis. Retrieved 2009-05-25.
- ^ "1p36 deletion syndrome". Orphanet. Retrieved 28 June 2022.