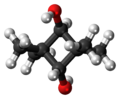
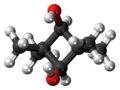
cis- (left) and trans-2,2,4,4-Tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol (right)
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2,4,4-Tetramethylcyclobutane-1,3-diol
| |||
| Other names
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyl-2,4-cyclobutanediol
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.219 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H16O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 144.214 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Crystalline white solid (powder) | ||
| Melting point | 126 to 134 °C (259 to 273 °F; 399 to 407 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 210 to 215 °C (410 to 419 °F; 483 to 488 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 51 °C (124 °F; 324 K) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | [1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
2,2,4,4-Tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol (CBDO) is an aliphatic diol. This diol is produced as a mixture of cis- and trans-isomers, depending on the relative stereochemistry of the hydroxyl groups. It is used as a monomer for the synthesis of polymeric materials, usually as an alternative to bisphenol A (BPA). CBDO is used in the production of tritan copolyester which is used as a BPA-free replacement for polycarbonate.