| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,3-Dimethylpentane | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.437 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 1206 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H16 | |
| Molar mass | 100.205 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 0.7076 g/mL (25 °C), 0.6413 (80 °C), 0.7380 (25 °C, 45 MPa), 0.6891 (80 °C, 45 MPa) (racemic)[1] |
| Boiling point | 89.7 °C (racemic)[2][3][4] |
| Vapor pressure | 2.35 psi (37.7 °C)[5] |
| Viscosity | 0.356 mPa s (30 °C), 0.232 (80 °C), 0.624 (30 °C, 60 MPa) (racemic)[1] |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
34.308 cal/K/mol (−189 °C), 51.647 (20 °C), 58.735 (86.6 °C) (racemic)[6] |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
71.02 cal/K/mol (25 °C) (racemic)[6] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H225, H304, H315, H335, H336, H410 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P273, P280, P301+P310, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P312, P321, P331, P332+P313, P362, P370+P378, P391, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | −7 °C (19 °F; 266 K)[5] |
| 337 °C (639 °F; 610 K)[5] | |
| Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
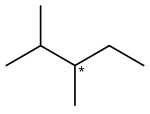
2,3-Dimethylpentane is an organic compound of carbon and hydrogen with formula C
7H
16, more precisely CH
3–CH(CH
3)–CH(CH
3)–CH
2–CH
3: a molecule of pentane with methyl groups –CH
3 replacing hydrogen atoms on carbon atoms 2 and 3. It is an alkane ("paraffin" in older nomenclature), a fully saturated hydrocarbon; specifically, one of the isomers of heptane.
Like typical alkanes, it is a colorless flammable compound; under common ambient conditions, it is a mobile liquid, less dense than water.[1]
2,3-Dimethylpentane is notable for being one of the two simplest alkanes with optical (enantiomeric) isomerism. The optical center is the middle carbon of the pentane backbone, which is connected to one hydrogen atom, one methyl group, one ethyl group –C
2H
5, and one isopropyl group –CH(CH
3)
2. The two enantiomers are denoted (3R)-2,3-dimethylpentane and (3S)-2,3-dimethylpentane (the other simplest chiral alkane is its structural isomer 3-methylhexane).
- ^ a b c Alfonso S. Pensado, María J. P. Comuñas, Luis Lugo, and Josefa Fernández (2005): "Experimental Dynamic Viscosities of 2,3-Dimethylpentane up to 60 MPa and from (303.15 to 353.15) K Using a Rolling-Ball Viscometer". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, volume 50, issue 3, pages 849–855. doi:10.1021/je049662k
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
nistwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
wienerwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
edgarwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Sigma Aldrich: 2,3-Dimethylpentane catalog entry. Accessed on 2018-11-06.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
finkewas invoked but never defined (see the help page).