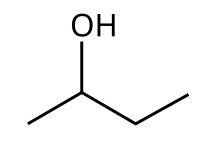
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butan-2-ol[2] | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 773649 1718764 (R) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.053 |
| EC Number |
|
| 1686 396584 (R) | |
| MeSH | 2-butanol |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 1120 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10O | |
| Molar mass | 74.123 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.808 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | −115 °C; −175 °F; 158 K |
| Boiling point | 98 to 100 °C; 208 to 212 °F; 371 to 373 K |
| 290 g/L[3] | |
| log P | 0.683 |
| Vapor pressure | 1.67 kPa (at 20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 17.6 [4] |
| −5.7683×10−5 cm3 mol−1 | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3978 (at 20 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
197.1 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
213.1 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−343.3 to −342.1 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−2.6611 to −2.6601 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H226, H319, H335, H336 | |
| P261, P305+P351+P338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 22 to 27 °C (72 to 81 °F; 295 to 300 K) |
| 405 °C (761 °F; 678 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1.7–9.8% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LCLo (lowest published)
|
16,000 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 10,670 ppm (mouse, 3.75 hr) 16,000 ppm (mouse, 2.67 hr)[5] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 150 ppm (450 mg/m3)[5] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 100 ppm (305 mg/m3) ST 150 ppm (455 mg/m3)[5] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
2000 ppm[5] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | inchem.org |
| Related compounds | |
Related butanols
|
n-Butanol Isobutanol tert-Butanol |
Related compounds
|
Butanone |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Butan-2-ol, or sec-butanol, is an organic compound with formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3. Its structural isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and tert-butanol. 2-Butanol is chiral and thus can be obtained as either of two stereoisomers designated as (R)-(−)-butan-2-ol and (S)-(+)-butan-2-ol. It is normally encountered as a 1:1 mixture of the two stereoisomers — a racemic mixture.
This secondary alcohol is a flammable, colorless liquid that is soluble in three parts water and completely miscible with organic solvents. It is produced on a large scale, primarily as a precursor to the industrial solvent methyl ethyl ketone.
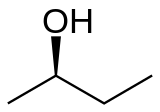 |

|
 |

|
| (R)-(−)-2-butanol | (S)-(+)-2-butanol |
- ^ "Alcohols Rule C-201.1". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry (The IUPAC 'Blue Book'), Sections A, B, C, D, E, F, and H. Oxford: Pergamon Press. 1979.
Designations such as isopropanol, sec-butanol, and tert-butanol are incorrect because there are no hydrocarbons isopropane, sec-butane, and tert-butane to which the suffix "-ol" can be added; such names should be abandoned. Isopropyl alcohol, sec-butyl alcohol, and tert-butyl alcohol are, however, permissible (see Rule C-201.3) because the radicals isopropyl, sec-butyl, and tert-butyl do exist
- ^ "2-butanol - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 12 October 2011.
- ^ Alger, Donald B. (November 1991). "The water solubility of butan-2-ol: A widespread error". Journal of Chemical Education. 68 (11): 939. Bibcode:1991JChEd..68..939A. doi:10.1021/ed068p939.1.
- ^ Serjeant, E.P., Dempsey B.; Ionisation Constants of Organic Acids in Aqueous Solution. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). IUPAC Chemical Data Series No. 23, 1979. New York, New York: Pergamon Press, Inc., p. 989
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0077". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
