| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 83.07% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A map showing the results of the Philippine presidential election by city and province and by region. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
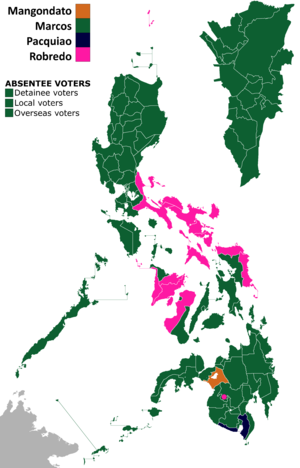
2022 Philippine vice presidential election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A map showing the results of the Philippine vice presidential election by city and province and by region. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
|
The 2022 Philippine presidential and vice presidential elections were held on May 9, 2022, as part of the 2022 general election. This was the 17th direct presidential election and 16th vice presidential election in the Philippines since 1935, and the sixth sextennial presidential and vice presidential election since 1992.
Incumbent president Rodrigo Duterte was ineligible for re-election because the president is limited to a single term under the 1987 Philippine Constitution. Incumbent vice president Leni Robredo was eligible for re-election but chose to run for the presidency instead. Therefore, this election determined the 17th president and the 15th vice president. The president and vice president are elected separately, so the two winning candidates can come from different political parties.
The election took place amidst the COVID-19 pandemic which had caused the country's economy to fall into recession.[1] Other key issues were the continuation of President Duterte's policies, a re-examination of the country's foreign relationships in response to its territorial dispute with China, management of the country's debt, rising inflation, and climate change.[2][3]
The ticket of former senator Bongbong Marcos and Davao City mayor Sara Duterte won the presidency and vice presidency respectively, defeating incumbent vice president Leni Robredo and incumbent senator Francis Pangilinan in a landslide. It was the first election since the establishment of the Fifth Republic in 1987 where the president and vice president were elected by a majority, and the first election since 2004 where the winning president and vice president came from the same presidential ticket.[4] The election saw the highest turnout since 1998, with about 56 million voters participating. Marcos received 31.6 million votes, the most votes ever cast for a candidate in a presidential election in the Philippines, while Duterte received 32.2 million votes, the most votes ever cast for a candidate in the country.
Marcos became the second president from Ilocos Norte after his father, former president Ferdinand Marcos,[5][6][7][8] while Duterte became the first vice president from Davao City, the third vice president to come from Mindanao after Emmanuel Pelaez and Teofisto Guingona Jr., and the youngest to be elected.[9] This also marked the return of the Marcos family to power for the first time since the People Power Revolution.[10][11] Marcos was inaugurated on June 30, 2022, while Duterte was inaugurated earlier on June 19, 2022.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
covidrecessionwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:29was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:30was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:31was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
proclamation-may25was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Verizon, Cliff (May 25, 2022). "Marcos officially declared Philippines' next president". Nikkei Asia. Retrieved May 26, 2022.
- ^ Morales, Neil Jerome (May 25, 2022). "Philippines Congress proclaims Marcos as next president". Reuters. Retrieved May 26, 2022.
- ^ Galvez, Daphne (May 25, 2022). "VP-elect Sara Duterte mum on why family members absent during proclamation". The Philippine Inquirer. Retrieved May 26, 2022.
- ^ Nalagon, Richy (June 21, 2022). "VP Sara's inauguration historic for Davaoeños". Manila Times. Archived from the original on June 22, 2022. Retrieved June 30, 2022.
- ^ "The son of late dictator Marcos has won the Philippines' presidential election". Associated Press. Manila. NPR. May 10, 2022. Archived from the original on May 12, 2022. Retrieved May 12, 2022.
- ^ "Biden, Xi congratulate Marcos Jr on Philippine presidential win". Al Jazeera. May 12, 2022. Archived from the original on May 12, 2022. Retrieved May 12, 2022.