| ||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential election | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Registered | 41,738,628 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 42.65% ( | |||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
484 of the 500 seat National Assembly 251 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
| United Nations Mission |
|
|
General elections were held in the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 20 December 2023. Combined elections were held for the President, 484 of the 500 members of the National Assembly, 700 of the 716 elected members of the 26 provincial assemblies, and for the first time under the new constitution, 951 members of a scaled down number of commune (municipal) councils. On election day, the Congolese government extended voting to 21 December for polling stations that had not opened on 20 December.[1][2] Agence France-Presse reported that some polling stations would open as late as 24 December.[3]
These elections were the first of the 4th election cycle under the 2006 constitution. Six more elections are scheduled to follow in 2024, five of which are indirect.
Elections were not organized in the territories of Kwamouth, Masisi, and Rutshuru due to ongoing armed conflict
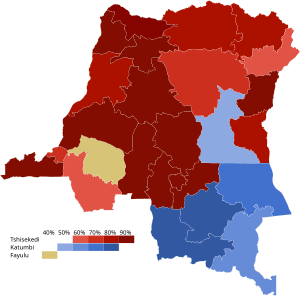
Incumbent President Félix Tshisekedi was provisionally declared the winner on 31 December by the Independent National Electoral Commission (CENI), winning about 73% of the vote.[4]
- ^ Rolley, Sonia; Kombi, Yassin; Erikas, Fiston Mahamba; Kambale, Mwisi; Kyala, Crispin; Bashizi, Arlette; Prentice, Alessandra; Felix, Bate (20 December 2023). Richardson, Alex; Chopra, Toby; Maler, Sandra; Wallis, Daniel (eds.). "Congo extends chaotic election as opposition calls for rerun". Reuters. Kinshasa and Goma. Retrieved 20 December 2023.
- ^ "Voting extends to 2nd day in Congo elections amid fraud claims". Anadolu Ajansi. Archived from the original on 21 December 2023. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ^ "Calls for restraint in DR Congo after tense vote". France 24. AFP. 23 December 2023. Archived from the original on 23 December 2023. Retrieved 23 December 2023.
- ^ "DR Congo election: President Felix Tshisekedi declared landslide winner". BBC. 31 December 2023. Archived from the original on 31 December 2023. Retrieved 31 December 2023.