| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
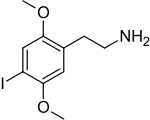
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(4-Iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethan-1-amine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.217.507 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10H14INO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 307.131 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 246 °C (475 °F; 519 K) | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| Legal status |
| ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
2C-I (2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodophenethylamine) is a phenethylamine of the 2C family with psychedelic properties, primarily used as a recreational drug.[1] It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, and is described in Shulgin's book PiHKAL (1991).
The substance is consumed as a recreational drug, and is circulated in the illicit market in a powder or liquid form. 2C-I is sometimes confused with other related chemical substances such as 25I-NBOMe (2C-I-NBOMe), nicknamed "Smiles" and "N-bomb" in the media.[2][3][4]
- ^ Bosak, Adam; LoVecchio, Frank; Levine, Michael (June 2013). "Recurrent Seizures and Serotonin Syndrome Following "2C-I" Ingestion". Journal of Medical Toxicology. 9 (2): 196–198. doi:10.1007/s13181-013-0287-x. ISSN 1556-9039. PMC 3657032. PMID 23378129.
- ^ "25I-NBOMe (2C-I-NBOMe): Fatalities / Deaths".
- ^ Weiss, Piper (September 20, 2012). 2C-I or 'Smiles': The New Killer Drug Every Parent Should Know About. Yahoo! News
- ^ Mackin, Teresa (October 9, 2012). Dangerous synthetic drug making its way across the country. Archived October 31, 2012, at the Wayback Machine WISH-TV

