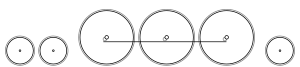
Locomotive wheel arrangement
4-6-2 (Pacific) Front of locomotive at left
First known tender engine version First use 1887 Country United States of America Railway Lehigh Valley Railroad Evolved from 4-6-0 Evolved to 4-6-4 Benefits Larger firebox than the 4-6-0 Drawbacks Required piloting (also known as double heading) when train lengths increased
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives , 4-6-2 wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. The 4-6-2 locomotive became almost globally known as a Pacific type after a locomotive built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in Philadelphia was shipped across the Pacific Ocean to New Zealand.[ 1] [ 2]
^ PRC Rail Consulting Ltd. "Steam Glossary" . The Railway Technical Website | PRC Rail Consulting Ltd . ^ Holland, D.F. (1971). Steam Locomotives of the South African Railways . Vol. 1: 1859–1910 (1st ed.). Newton Abbott, England: David & Charles . pp. 69–77, 88–89, 101–103, 128–130, 137–139. ISBN 978-0-7153-5382-0