| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
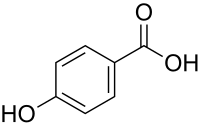
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | |
| Other names
p-Hydroxybenzoic acid
para-Hydroxybenzoic acid PHBA 4-hydroxybenzoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.550 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 138.122 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.46 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 214.5 °C (418.1 °F; 487.6 K) |
| Boiling point | N/A, decomposes[1] |
| 0.5 g/100 mL | |
| Solubility |
|
| log P | 1.58 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.54 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Irritant |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
2200 mg/kg (oral, mouse) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | HMDB |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters, known as parabens, which are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin, and with 3-hydroxybenzoic acid.
- ^ "4-Hydroxybenzoic acid" (PDF). International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
