| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
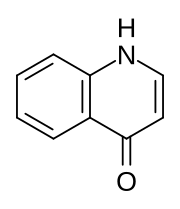
| Preferred IUPAC name
Quinolin-4(1H)-one | |
| Other names
1H-Quinolin-4-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.336 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H7NO | |
| Molar mass | 145.161 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 208–210 °C (406–410 °F; 481–483 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
4-Quinolone is an organic compound derived from quinoline. It and 2-quinolone are the two most important parent (meaning simplified) quinolones. 4-Quinolone exists in equilibrium with a minor tautomer, 4-hydroxyquinoline (CAS#611-36-9). Aside from pedagogical interest, 4-quinolone is of little intrinsic value but its derivatives, the 4-quinolone antibiotics, represent a large class of important drugs.[1]

- ^ Andriole, VT The Quinolones. Academic Press, 1989.