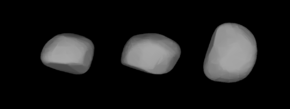
 A three-dimensional model of 532 Herculina based on its light curve | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Max Wolf |
| Discovery date | 20 April 1904 |
| Designations | |
| (532) Herculina | |
| Pronunciation | /hɜːrkjʊˈlaɪnə/ |
| 1904 NY | |
| Main belt | |
| Adjectives | Herculinian /hɜːrkjʊˈlɪniən/ |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 31 July 2016 (JD 2457600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 111.97 yr (40897 d) |
| Aphelion | 3.26056 AU (487.773 Gm) |
| Perihelion | 2.28601 AU (341.982 Gm) |
| 2.7732838 AU (414.87735 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.1757028 |
| 4.62 yr (1686.9 d) (1684.34607 d) | |
| 131.03906° | |
| 0° 12m 48.272s / day | |
| Inclination | 16.31351° |
| 107.55583° | |
| 76.09745° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| 167.791±0.890 km[1] 222.19 km[2] 217.49 ± 5.10 km[3] 191 ± 4 km[4] | |
| Mass | (2.29±0.20)×1019 kg[2] (1.15±0.28)×1019 kg[3] (1.0051 ± 0.1108/0.1567)×1019 kg[4] |
Mean density | 4.0 g/cm3[2] 2.12±0.53 g/cm3[3] 2.755 ± 0.304/0.429 g/cm3[4] |
| 9.405 h (0.3919 d)[1] | |
| 0.285±0.029[1] | |
| S[1] | |
| 8.82 to 11.99[5] | |
| 5.92[1] | |
| 0.228" to 0.073" | |
532 Herculina /hɜːrkjʊˈlaɪnə/ is a large asteroid, with a diameter of around 200 km.
- ^ a b c d e f "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 532 Herculina (1904 NY)" (2008-11-17 last obs). Retrieved 8 May 2016.
- ^ a b c Masses and densities of minor planets Archived 2011-06-04 at the Wayback Machine - Yu. Chernetenko, O. Kochetova, and V. Shor
- ^ a b c Carry, B. (December 2012), "Density of asteroids", Planetary and Space Science, vol. 73, pp. 98–118, arXiv:1203.4336, Bibcode:2012P&SS...73...98C, doi:10.1016/j.pss.2012.03.009. See Table 1.
- ^ a b c Fienga, A.; Avdellidou, C.; Hanuš, J. (February 2020). "Asteroid masses obtained with INPOP planetary ephemerides". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 492 (1). doi:10.1093/mnras/stz3407.
- ^ "Bright Minor Planets 2005". Minor Planet Center. Archived from the original on 29 September 2008. Retrieved 21 May 2008.