 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
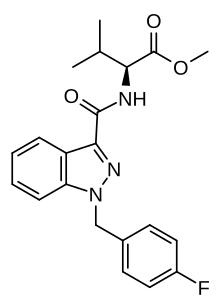
| Formula | C21H22FN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 383.423 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
AMB-FUBINACA (also known as FUB-AMB and MMB-FUBINACA[3]) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is a potent agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with Ki values of 10.04 nM at CB1 and 0.786 nM at CB2 and EC50 values of 0.5433 nM at CB1 and 0.1278 nM at CB2,[4] and has been sold online as a designer drug.[5][6][7][8] It was originally developed by Pfizer which described the compound in a patent in 2009, but was later abandoned and never tested on humans.[9] AMB-FUBINACA was the most common synthetic cannabinoid identified in drug seizures by the Drug Enforcement Administration in 2017 and the first half of 2018.[10]
- ^ Anvisa (2023-07-24). "RDC Nº 804 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-07-25). Archived from the original on 2023-08-27. Retrieved 2023-08-27.
- ^ "Substance Details FUB-AMB". Retrieved 2024-01-22.
- ^ Pulver B, Fischmann S, Gallegos A, Christie R (March 2023). "EMCDDA framework and practical guidance for naming synthetic cannabinoids". Drug Testing and Analysis. 15 (3): 255–276. doi:10.1002/dta.3403. PMID 36346325.
- ^ Gamage TF, Farquhar CE, Lefever TW, Marusich JA, Kevin RC, McGregor IS, et al. (May 2018). "Molecular and Behavioral Pharmacological Characterization of Abused Synthetic Cannabinoids MMB- and MDMB-FUBINACA, MN-18, NNEI, CUMYL-PICA, and 5-Fluoro-CUMYL-PICA". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 365 (2): 437–446. doi:10.1124/jpet.117.246983. PMC 5932312. PMID 29549157.
- ^ "FUB-AMB". Cayman Chemical. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- ^ Akamatsu S, Yoshida M (January 2016). "Fragmentation of synthetic cannabinoids with an isopropyl group or a tert-butyl group ionized by electron impact and electrospray". Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 51 (1): 28–32. Bibcode:2016JMSp...51...28A. doi:10.1002/jms.3722. PMID 26757069.
- ^ Banister SD, Longworth M, Kevin R, Sachdev S, Santiago M, Stuart J, et al. (September 2016). "Pharmacology of Valinate and tert-Leucinate Synthetic Cannabinoids 5F-AMBICA, 5F-AMB, 5F-ADB, AMB-FUBINACA, MDMB-FUBINACA, MDMB-CHMICA, and Their Analogues". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 7 (9): 1241–1254. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00137. PMID 27421060.
- ^ Wagmann L, Stiller RG, Fischmann S, Westphal F, Meyer MR (October 2022). "Going deeper into the toxicokinetics of synthetic cannabinoids: in vitro contribution of human carboxylesterases". Archives of Toxicology. 96 (10): 2755–2766. doi:10.1007/s00204-022-03332-z. PMC 9352624. PMID 35788413.
- ^ Santora M (2016-12-14). "Drug 85 Times as Potent as Marijuana Caused a 'Zombielike' State in Brooklyn". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
- ^ Yin S (2019). "Adolescents and Drug Abuse: 21st Century Synthetic Substances". Clinical Pediatric Emergency Medicine. 20 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1016/j.cpem.2019.03.003. S2CID 88290992.