| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
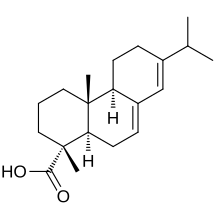
| IUPAC name
Abieta-7,13-dien-18-oic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,4aR,4bR,10aR)-1,4a-Dimethyl-7-(propan-2-yl)-1,2,3,4,4a,4b,5,6,10,10a-decahydrophenanthrene-1-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Abietinic acid; Sylvic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.436 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H30O2 | |
| Molar mass | 302.458 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow resinous powder, crystals or chunks. Monoclinic plates (from EtOH/water). Colorless solid when pure. |
| Density | 1.06 g/mL |
| Melting point | 172–175 °C (342–347 °F; 445–448 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 250 °C; 482 °F; 523 K |
| Insoluble[2] | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Very soluble in acetone, petroleum ether, Et2O, and ethanol |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Irritant |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H317 | |
| P261, P272, P280, P302+P352, P321, P333+P313, P363, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Abietic acid (also known as abietinic acid or sylvic acid) is a mild organic acid found in coniferous trees.
It is a commercially important component of paints, soaps, foods, and soldering flux, and is the primary component of resin acid.
- ^ National Toxicology Program, Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health (NTP). 1992. National Toxicology Program Chemical Repository Database. Research Triangle Park, North Carolina
- ^ a b Merck Index, 12th Edition, 3. Abietic Acid
