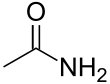
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Acetamide[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Ethanamide | |||
| Other names
Acetic acid amide
Acetylamine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.430 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H5NO | |||
| Molar mass | 59.068 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless, hygroscopic solid | ||
| Odor | odorless mouse-like with impurities | ||
| Density | 1.159 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | 79 to 81 °C (174 to 178 °F; 352 to 354 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 221.2 °C (430.2 °F; 494.3 K) (decomposes) | ||
| 2000 g L−1[2] | |||
| Solubility | ethanol 500 g L−1[2] pyridine 166.67 g L−1[2] soluble in chloroform, glycerol, benzene[2] | ||
| log P | −1.26 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 1.3 Pa | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 15.1 (25 °C, H2O)[3] | ||
| −0.577 × 10−6 cm3 g−1 | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.4274 | ||
| Viscosity | 2.052 cP (91 °C) | ||
| Structure | |||
| trigonal | |||
| Thermochemistry[4] | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
91.3 J·mol−1·K−1 | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
115.0 J·mol−1·K−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−317.0 kJ·mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H351 | |||
| P201, P202, P281, P308+P313, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 126 °C (259 °F; 399 K) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
7000 mg kg−1 (rat, oral) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Acetamide (systematic name: ethanamide) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CONH2. It is an amide derived from ammonia and acetic acid. It finds some use as a plasticizer and as an industrial solvent.[5] The related compound N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA) is more widely used, but it is not prepared from acetamide. Acetamide can be considered an intermediate between acetone, which has two methyl (CH3) groups either side of the carbonyl (CO), and urea which has two amide (NH2) groups in those locations. Acetamide is also a naturally occurring mineral[6] with the IMA symbol: Ace.[7]
- ^ "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 841. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c d The Merck Index, 14th Edition, 36
- ^ Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–88. ISBN 9781498754293.
- ^ John Rumble (June 18, 2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–3. ISBN 978-1138561632.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ullmannwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Mindat: Naturally occurring acetamide
- ^ Warr, L.N. (2021). "IMA-CNMNC approved mineral symbols". Mineralogical Magazine. 85 (3): 291–320. Bibcode:2021MinM...85..291W. doi:10.1180/mgm.2021.43. S2CID 235729616.