| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Acetic anhydride | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Ethanoic anhydride | |
| Other names
Ethanoyl ethanoate
Acetic acid anhydride Acetyl acetate Acetyl oxide Acetic oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.241 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1715 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
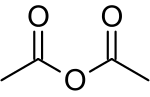
| C4H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 102.089 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.082 g cm−3, liquid |
| Melting point | −73.1 °C (−99.6 °F; 200.1 K) |
| Boiling point | 139.8 °C (283.6 °F; 412.9 K) |
| 2.6 g/100 mL, reacts (see text) | |
| Vapor pressure | 4 mmHg (20 °C)[1] |
| −52.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3901 |
| Thermochemistry[2] | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−624.4 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| Legal status |
|
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H226, H302, H314, H330 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P330, P363, P370+P378, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 49 °C (120 °F; 322 K) |
| 316 °C (601 °F; 589 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 2.7–10.3% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
1000 ppm (rat, 4 h)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 5 ppm (20 mg/m3)[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
C 5 ppm (20 mg/m3)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
200 ppm[1] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0209 |
| Related compounds | |
Related acid anhydrides
|
Propionic anhydride |
Related compounds
|
Acetic acid Acetyl chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air.
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0003". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ John Rumble (June 18, 2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–3. ISBN 978-1138561632.
- ^ "Acetic anhydride". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
