 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lithostat |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.104 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
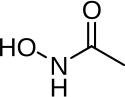
| Formula | C2H5NO2 |
| Molar mass | 75.067 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Acetohydroxamic acid (also known as AHA or by the trade name Lithostat) is a drug that is a potent and irreversible enzyme inhibitor of the urease enzyme in various bacteria and plants; it is usually used for urinary tract infections. The molecule is similar to urea but is not hydrolyzable by urease;[1] it thus disrupts the bacteria's metabolism through competitive inhibition.
- ^ Fishbein WN, Carbone PP (June 1965). "Urease Catalysis. Ii. Inhibition of the Enzyme by Hydroxyurea, Hydroxylamine, and Acetohydroxamic Acid". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 240: 2407–14. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)97338-2. PMID 14304845.