| |||
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Acetone[7]
| |||
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propan-2-one[8] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-Propanone | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 635680 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.602 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 1466 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Acetone | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1090 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6O | |||
| Molar mass | 58.080 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Odor | Pungent, fruity[9] | ||
| Density | 0.7845 g/cm3 (25 °C)[10] | ||
| Melting point | −94.9 °C (−138.8 °F; 178.2 K)[10] | ||
| Boiling point | 56.08 °C (132.94 °F; 329.23 K)[10] | ||
| Miscible[10] | |||
| Solubility | Miscible in benzene, diethyl ether, methanol, chloroform, ethanol[10] | ||
| log P | −0.24[11] | ||
| Vapor pressure |
| ||
| Acidity (pKa) | |||
| −33.8·10−6 cm3/mol[14] | |||
| Thermal conductivity | 0.161 W/(m·K) (25 °C)[15] | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3588 (20 °C)[10] | ||
| Viscosity | 0.306 mPa·s (25 °C)[16] | ||
| Structure | |||
| Trigonal planar at C2 | |||
| Dihedral at C2 | |||
| 2.88 D[17] | |||
| Thermochemistry[18] | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
126.3 J/(mol·K) | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
199.8 J/(mol·K) | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−248.4 kJ/mol | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−1.79 MJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Highly flammable | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H302, H319, H336, H373 | |||
| P210, P235, P260, P305+P351+P338 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −20 °C (−4 °F; 253 K)[19] | ||
| 465[19] °C (869 °F; 738 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 2.5–12.8%[19] | ||
Threshold limit value (TLV)
|
250 ppm[20] (STEL), 500 ppm[20] (C) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
| ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
20,702 ppm (rat, 8 h)[21] | ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
45,455 ppm (mouse, 1 h)[21] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
1000 ppm (2400 mg/m3)[3] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 250 ppm (590 mg/m3)[3] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
2500 ppm[3] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Acetone (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
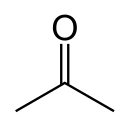
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CO.[22] It is the simplest and smallest ketone (>C=O). It is a colorless, highly volatile, and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour, very reminiscent of the smell of pear drops.
Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and for production of methyl methacrylate and bisphenol A, which are precursors to widely used plastics.[23][24] It is a common building block in organic chemistry. It serves as a solvent in household products such as nail polish remover and paint thinner. It has volatile organic compound (VOC)-exempt status in the United States.[25]
Acetone is produced and disposed of in the human body through normal metabolic processes. It is normally present in blood and urine. People with diabetic ketoacidosis produce it in larger amounts. Ketogenic diets that increase ketone bodies (acetone, β-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid) in the blood are used to counter epileptic attacks in children who suffer from refractory epilepsy.[26]
- ^ The Merck Index, 15th Ed. (2013), p. 13, Acetone Monograph 65, O'Neil: The Royal Society of Chemistry.(subscription required)
- ^ a b c d Acetone in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD)
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0004". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Klamt, Andreas (2005). COSMO-RS: From Quantum Chemistry to Fluid Phase Thermodynamics and Drug Design. Elsevier. pp. 92–94. ISBN 978-0-444-51994-8.
- ^ Myers, Richard L. (2007). The 100 Most Important Chemical Compounds: A Reference Guide. Greenwood. pp. 4–6. ISBN 978-0-313-08057-9.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
gorman1962was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ ChemSpider lists 'acetone' as a valid, expert-verified name for what would systematically be called 'propan-2-one'.
- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 723. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
smellwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f Haynes, p. 3.4
- ^ Haynes, p. 5.173
- ^ Chiang, Yvonne; Kresge, A. Jerry; Tang, Yui S.; Wirz, Jakob (1984). "The pKa and keto-enol equilibrium constant of acetone in aqueous solution". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 106 (2): 460–462. doi:10.1021/ja00314a055.
- ^ Bordwell, Frederick G. (1988). "Equilibrium acidities in dimethyl sulfoxide solution". Accounts of Chemical Research. 21 (12): 456–463. doi:10.1021/ar00156a004. S2CID 26624076.
- ^ Haynes, p. 3.576
- ^ Haynes, p. 6.254
- ^ Haynes, p. 6.243
- ^ Haynes, p. 9.60
- ^ Haynes, pp. 5.3, 5.67
- ^ a b c Haynes, p. 15.13
- ^ a b Haynes, p. 16.34
- ^ a b c "Acetone". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Allen, P .W.; Bowen, H. J. M.; Sutton, L. E.; Bastiansen, O. (1952). "The molecular structure of acetone". Transactions of the Faraday Society. 48: 991. doi:10.1039/TF9524800991.
- ^ Acetone, World Petrochemicals report, January 2010
- ^ Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.
- ^ "Update: U.S. EPA Exempt Volatile Organic Compounds". American Coatings Association. 2018-01-30. Archived from the original on 2021-02-08. Retrieved 2019-03-20.
- ^ Freeman, JM; Kossoff, EH; Hartman, AL (Mar 2007). "The ketogenic diet: one decade later". Pediatrics. 119 (3): 535–43. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-2447. PMID 17332207. S2CID 26629499.