 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /eɪˈsaɪkloʊvɪər/ |
| Trade names | Zovirax, others[1] |
| Other names | Acycloguanosine, acyclovir (BAN UK), acyclovir (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | |
| MedlinePlus | a681045 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, by mouth, topical, eye ointment |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 15–20% (by mouth)[3] |
| Protein binding | 9–33%[3] |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 2–4 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (62–90% as unchanged drug) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| PubChem SID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.056.059 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
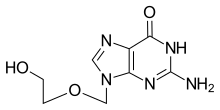
| Formula | C8H11N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 225.208 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 256.5 °C (493.7 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Aciclovir, also known as acyclovir,[4] is an antiviral medication.[5] It is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles.[6] Other uses include prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following transplant and severe complications of Epstein–Barr virus infection.[6][7] It can be taken by mouth, applied as a cream, or injected.[6]
Common side effects include nausea and diarrhea.[6] Potentially serious side effects include kidney problems and low platelets.[6] Greater care is recommended in those with poor liver or kidney function.[6] It is generally considered safe for use in pregnancy with no harm having been observed.[6][8] It appears to be safe during breastfeeding.[9][10] Aciclovir is a nucleoside analogue that mimics guanosine.[6] It works by decreasing the production of the virus's DNA.[6]
Aciclovir was patented in 1974 by Burroughs Wellcome, and approved for medical use in 1981.[11] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[12] It is available as a generic medication and is marketed under many brand names worldwide.[1] In 2022, it was the 134th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 4 million prescriptions.[13][14]
- ^ a b "Aciclovir". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 6 September 2015.
- ^ "Skin health". Health Canada. 9 May 2018. Retrieved 13 April 2024.
- ^ a b "Zovirax (acyclovir) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 19 February 2014. Retrieved 5 February 2014.
- ^ Kevin ES. "The Aciclovir" (in German). Kevin. Retrieved 25 May 2017.
- ^ de Clercq E, Field HJ (5 October 2005). "Antiviral prodrugs – the development of successful prodrug strategies for antiviral chemotherapy". British Journal of Pharmacology. Vol. 147, no. 1. Wiley-Blackwell (published January 2006). pp. 1–11. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706446. PMC 1615839. PMID 16284630.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Acyclovir". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 2015-01-05. Retrieved Jan 1, 2015.
- ^ Rafailidis PI, Mavros MN, Kapaskelis A, Falagas ME (November 2010). "Antiviral treatment for severe EBV infections in apparently immunocompetent patients". Journal of Clinical Virology. 49 (3): 151–157. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2010.07.008. PMID 20739216.
- ^ "Prescribing medicines in pregnancy database". Australian Government. 3 March 2014. Archived from the original on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
- ^ Hamilton R (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 59. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ^ "Acyclovir use while Breastfeeding". Mar 10, 2015. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 8 March 2016.
Even with the highest maternal dosages, the dosage of acyclovir in milk is only about 1% of a typical infant dosage and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 504. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Acyclovir Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.