This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (December 2016) |  |
| |
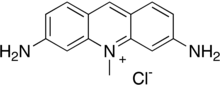
 Sample of pure acriflavine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,6-Diamino-10-methylacridin-10-ium chloride | |
| Other names
Acriflavinium chloride (INN)
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.211.047 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H14ClN3 | |
| Molar mass | 259.74 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| R02AA13 (WHO) QG01AC90 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Acriflavine (INN: acriflavinium chloride) is a topical antiseptic. It has the form of an orange or brown powder. It may be harmful in the eyes or if inhaled. It is a dye and it stains the skin and may irritate. The hydrochloride form is more irritating than the neutral form. It is derived from acridine. Commercial preparations are often mixtures with proflavine.[1] It is known by a variety of commercial names.