 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.192 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
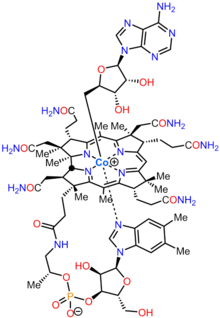
| Formula | C72H100CoN18O17P |
| Molar mass | 1579.608 g·mol−1 |
| |
| | |
Adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), also known as coenzyme B12, cobamamide, and dibencozide, is, along with methylcobalamin (MeCbl), one of the biologically active forms of vitamin B12.[1]
Adenosylcobalamin participates as a cofactor in radical-mediated 1,2-carbon skeleton rearrangements. These processes require the formation of the deoxyadenosyl radical through homolytic dissociation of the carbon-cobalt bond. This bond is exceptionally weak, with a bond dissociation energy of 31 kcal/mol, which is further lowered in the chemical environment of an enzyme active site.[2] An enzyme that uses adenosylcobalamin as a cofactor is methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MCM).
Further experimentation has also determined adenosylcobalamin's role in regulating expression of some bacterial genes. By binding to CarH,[clarification needed] AdoCbl can modulate carotenoid genes, which confer warm colors onto various plants. Carotenoid transcription is activated by sunlight, due to the response from AdoCbl.[3] There are other photoreceptors across different bacterial communities, aside from CarH, that also have reactive capability when bound to AdoCbl. For instance, AerR is another factor that uses AdoCbl to give off purple pigmentation. Additional examination of adenosylcobalamin-bound enzymes and the development of this cofactor over time may prove to hold regulatory function of DNA and RNA.[4]
- ^ Marsh EN, Meléndez GD (November 2012). "Adenosylcobalamin enzymes: theory and experiment begin to converge". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics. 1824 (11): 1154–1164. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.03.012. PMC 3580769. PMID 22516318.
- ^ Kräutler B, Arigoni D, Golding BT (1998). Vitamin B12 and B12-proteins : lectures presented at the 4th European Symposium on Vitamin B12 and B12-Proteins. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. ISBN 9783527612192. OCLC 212131311.
- ^ Jost M (April 1, 2015). "An Old Cofactor in a New Light: Adenosylcobalamin in Light-Dependent Gene Regulation". The FASEB Journal. 29. doi:10.1096/fasebj.29.1_supplement.573.25. S2CID 89044509.
- ^ Chemaly SM (October 2016). "New light on vitamin B12: The adenosylcobalamin-dependent photoreceptor protein CarH". South African Journal of Science. 112 (9–10): 9. doi:10.17159/sajs.2016/20160106. S2CID 90441731.