 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.267 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
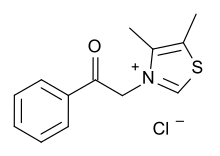
| Formula | C13H14ClNOS |
| Molar mass | 267.77 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Alagebrium (formerly known as ALT-711, dimethyl-3-N-phenacylthiazolium chloride) was a drug candidate developed by Alteon, Inc. It was the first drug candidate to be clinically tested for the purpose of breaking the crosslinks caused by advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs), thereby reversing one of the main mechanisms of aging.[1] Through this effect Alagebrium is designed to reverse the stiffening of blood vessel walls that contributes to hypertension and cardiovascular disease, as well as many other forms of degradation associated with protein crosslinking.[2] Alagebrium has proven effective in reducing systolic blood pressure[3] and providing therapeutic benefit for patients with diastolic heart failure.[4]
- ^ "R&D overview: A.G.E. crosslink breakers and Alagebrium". Alteon Corporation. Archived from the original on 1 July 2007. Retrieved 4 July 2007.
- ^ "Product Candidate: A.G.E. crosslink breakers". Alteon Corporation. Archived from the original on 1 July 2007. Retrieved 4 July 2007.
- ^ Bakris GL, Bank AJ, Kass DA, Neutel JM, Preston RA, Oparil S (December 2004). "Advanced glycation end-product cross-link breakers. A novel approach to cardiovascular pathologies related to the aging process". American Journal of Hypertension. 17 (12 Pt 2): 23S–30S. doi:10.1016/j.amjhyper.2004.08.022. PMID 15607432.
- ^ Little WC, Zile MR, Kitzman DW, Hundley WG, O'Brien TX, Degroof RC (April 2005). "The effect of alagebrium chloride (ALT-711), a novel glucose cross-link breaker, in the treatment of elderly patients with diastolic heart failure". Journal of Cardiac Failure. 11 (3): 191–195. doi:10.1016/j.cardfail.2004.09.010. PMID 15812746.