 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lotronex |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601230 |
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50–60% |
| Protein binding | 82% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (including CYP2C9, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2) |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5–1.7 hours |
| Excretion | Renal 73%, faecal 24% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
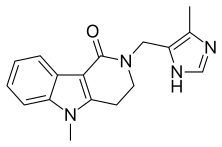
| Formula | C17H18N4O |
| Molar mass | 294.358 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Alosetron, sold under the brand name Lotronex among others, is a 5-HT3 antagonist used for the management of severe diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in females only.
It was patented in 1987 and approved for medical use in 2002.[2] It is currently marketed by Prometheus Laboratories Inc. (San Diego). Alosetron was withdrawn from the market in 2000 owing to the occurrence of serious life-threatening gastrointestinal adverse effects, but was reintroduced in 2002 with availability and use restricted.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 448. ISBN 9783527607495.